
Turn to a solutions provider that can deliver expert guidance on tax depreciation and other cost recovery issues, so your firm can better serve business clients. Section 179 is also an immediate expense deduction, similar to bonus depreciation. In the coming years, as bonus depreciation phases out, some taxpayers may be able to maintain some initial-year expensing through section 179 rules. The complexities start to emerge given that there are rules as to which assets, and how much money, can be depreciated each year on a client’s taxes. We will explore how to weed out the time-consuming labor that can come with tax depreciation and how tax professionals can better assist clients in making more tax-efficient business decisions.
Accumulated Depreciation, Carrying Value, and Salvage Value
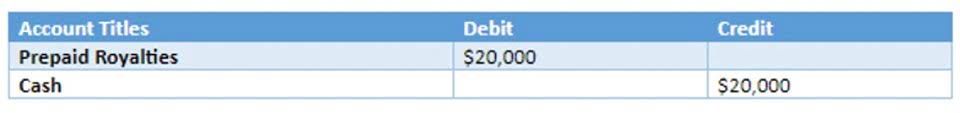
As you probably know, the basic calculation of depreciation involves dividing the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life using a suitable depreciation method. To estimate the amount of profit and assets of any business correctly, we must know how to differentiate between assets that should be depreciated in the accounting books (i.e., depreciable assets) and non-depreciable assets. If gains on Section 1231 properties exceed the adjusted basis and the depreciation amount, the earnings are capital gains. That said, if losses are recorded on such a property whereby the loss is ordinary, it is fully deductible against the income.

What kind of assets can you depreciate?

Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
- Sankofa does not claim the section 179 deduction and the machines do not qualify for a special depreciation allowance.
- This chapter explains how to determine which MACRS depreciation system applies to your property.
- On February 1, 2021, Larry House, a calendar year taxpayer, leased and placed in service an item of listed property with an FMV of $3,000.
- You can account for uses that can be considered part of a single use, such as a round trip or uninterrupted business use, by a single record.
- You are allowed to depreciate the value of a building you’ve purchased–but the value of the land it’s on can’t be written off.
Best Accounting Software for Small Businesses of 2024
This means that there will be a large difference between tax expense and taxable income at the beginning of the accounting period. Because large losses are realized early, the tax benefit will be spread over a longer period. Instead of recording an asset’s entire expense when it’s first bought, depreciation distributes the expense over multiple years. Depreciation quantifies the declining value of a business asset, based on its useful life, and balances out the revenue it’s helped to produce. MACRS allows you to track and record depreciation using either the straight-line method or the double declining balance method. The method depreciable asset used by the IRS is called The Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS).
Sum-of-the-years depreciation

A list of depreciable assets may include tangible assets such as buildings, machinery, equipment, and furniture. Organizations purchase these assets to https://www.bookstime.com/ fulfill a particular business purpose. They can start depreciating such assets once they become available and ready to use. As these tangible assets age, they become less effective, and their value falls.
For a discussion of when property is placed in service, see When Does Depreciation Begin and End, earlier. Even if the requirements explained in the preceding discussions are met, you cannot depreciate the following property. Generally, containers for the products you sell are part of inventory and you cannot depreciate them. However, you can depreciate containers used to ship your products if they have a life longer than 1 year and meet the following requirements. To be depreciable, the property must meet all the following requirements.
Depreciation Is a Process of Cost Allocation
Depreciable business assets are assets that have a lifespan and can be considered a business expense. These assets can be depreciated on a business’s taxes, which means that the tax benefits of the business expense are spread out over multiple years. Let’s say that, according to the manufacturer, the bouncy castle can be used a total of 100,000 hours before its useful life is over. To get the depreciation cost of each hour, we divide the book value over the units of production expected from the asset.
When figuring the number of years remaining, you must take into account the convention used in the year you placed the property in service. If the number of years remaining is less than 1, the depreciation rate for https://x.com/BooksTimeInc that tax year is 1.0 (100%). Instead of using the rates in the percentage tables to figure your depreciation deduction, you can figure it yourself.

- The cost of land generally includes the cost of clearing, grading, planting, and landscaping.
- Since it’s used to reduce the value of the asset, accumulated depreciation is a credit.
- Consumer durable property does not include real property, aircraft, boats, motor vehicles, or trailers.
- Section 1.168(i)-6 of the regulations does not reflect this change in law..
- You must generally depreciate the carryover basis of property acquired in a like-kind exchange or involuntary conversion over the remaining recovery period of the property exchanged or involuntarily converted.
You must make the election on a timely filed return (including extensions) for the year of replacement. The election must be made separately by each person acquiring replacement property. In the case of a partnership, S corporation, or consolidated group, the election is made by the partnership, by the S corporation, or by the common parent of a consolidated group, respectively. You reduce the adjusted basis ($1,000) by the depreciation claimed in the first year ($200).